...
The matching password for the user of the service.
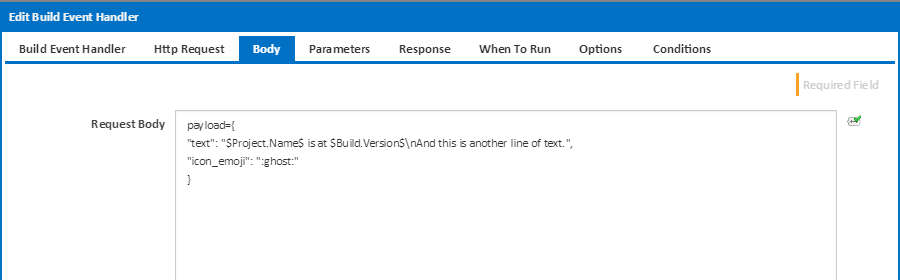
Request Body
The request body is where the information for the request is placed. In the case above, the request expects a JSON object called payload. The object has two properties called name and icon_emoji - each with values provided for the given request.
The values can have Continua CI variables included in them so that build information can be passed onto other systems. In the above example the text message passed onto the HTTP request includes the project name and build version number.
Querystring Parameters
These parameters should be provided in <name>=<value> format. Each parameter will be added to the query string which is sent as part of the request. Adding query string parameters here means that you do not have to get the formatting correct for the HTTP query string yourself. All escaping is handled for you when using the querystring parameter entry box.
...
Use this to add any get/post parameters for to the request. These are simple parameters that the endpoint may require or use to understand the request being made of it. These parameters should be provided in <name>=<value> format with each pair on a separate line.
Headers
Allows for adding you to add header parameters for to the request. These should be entered in the <name>=<value> format with each pair on a separate line.
Cookies
Allows for adding you to add cookie parameters for to the request. These should be entered in the <name>=<value> format with each pair on a separate line.
Response Variables
Allows for These can be used to extracting values from JSON or XML responses and placing place them into configuration variables the configuration has access to. To extact extract values from the JSON and XML responses, JSONpath and XPath can be used. Each has their own syntax for extracting values for nodes within the objects they represent. Below is a list of some of the syntax allowed by each.
| XPath | JSONPath | Description |
| / | $ | The base node in the object. |
| . | @ | The current object in the node path. |
| / | . or [] | Accessing a child node, or specific child node |
| .. | n/a | Accessing the parent of the current node. |
| // | .. | Recursive child decent. |
| * | * | Wildcard operator to access any node. |
| @ | n/a | Accessing an attribute. |
| [] | [] | Accessing an element within a list of nodes. |
| | | [,] | Union of two sets of nodes. |
| n/a | [start:end:step] | Accessing elements as a slice of a set of elements. |
| [] | ?() | Accessing nodes with a filter applied. |
Listed below is an example response in JSON and XML.
...
|
|---|
|
|---|
The following are example XPath and JSONPaths that could be used on the above responses to extract information your looking for.
| XPath | JSONPath | Result |
/messages/staging/author | $.messages.staging[*].author | The authors of all messages sent to staging |
//author | $..author | All the authors of all messages |
/messages/* | $.messages.* | All channels messages were sent to. Staging and production. |
/messages//category | $.messages..category | The categories of all messages. |
//staging[3] | $..staging[2] | The third message sent to staging. |
//staging[last()] | $..staging[(@.length-1)]$..staging[-1:] | The last message sent to staging. |
//staging[position()<3] | $..staging[0,1]$..staging[:2] | The first two messages sent to staging. |
//staging[category="error"] | $..staging[?(@.category="error")] | All the messages sent to staging with an error category. This would return no values. |
//* | $..* | All nodes in the response. |
Successful Response Statues
Check each of the response statuses that would mean the request has been successful. If the request returns a status that is not checked then the build event handler will report an error. If errors are to be treated as failures then the build event handler will fail the build at his point.
When To Run
You can specfy specify when the build event handler runs by linking it to a Build Event on the When To Run tab
Build Event
Select the event which triggers the tag action. You can choose one of the following Build Events:
- On Build Created
- On Before Build Queued
- On Before Build Start
- On After Build Started
- On Before Stage Start
- On Sending Stage To Agent
- On Stage Completed
- On Build Pending Promotion
- On Before Build Continue
- On After Build Continued
- On Build Stopping
- On Build Completed
Stage
For stage events, select the stage this applies to, or "(all stages)" to trigger the tagging action for all stages
Build Status
For "On Stage Completed" and "On Build Completed", you can choose to trigger the tagging action when the build is Successful or has Failed.
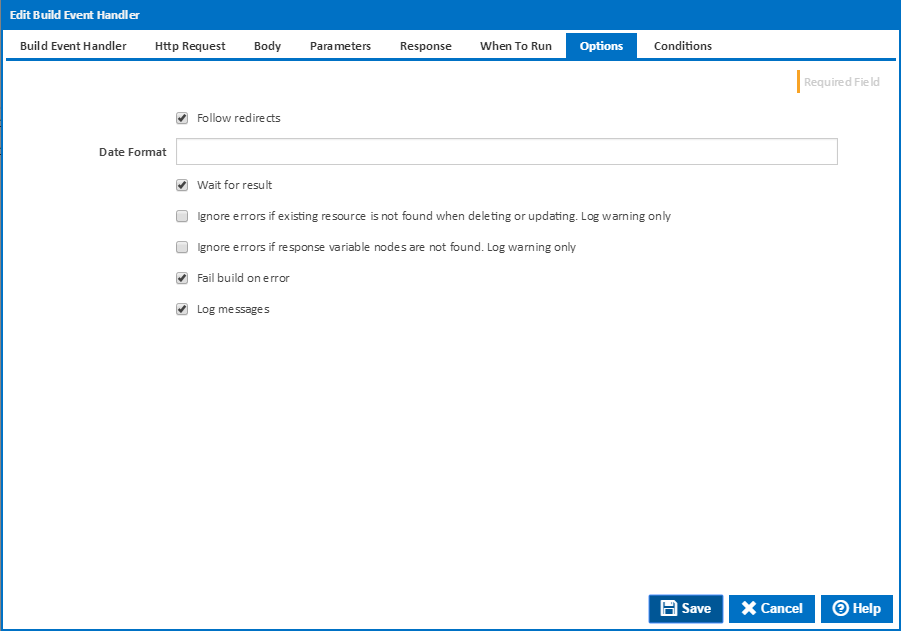
Options
Follow redirects
Clear this option to fail if the HTTP endpoint causes a redirection.
Date Format
Optionally specify the date time format used in your request body. If you leave this blank the action will attempt to parse various formats in the invariant culture.
Wait for result
Clear this option to run the tagging action in a separate thread if you don't care about the result eg. whether the action fails or not.
Ignore errors if existing resource is not found when deleting or updating. Log warning only
An error result will be returned if a Not Found status code is returned when using DELETE or PATCH methods. Tick this option to ignore these errors, only logging a warning to the build log. This is only available if Wait for result is ticked..
Ignore errors if existing response variable nodes are not found. Log warning only
An error result will be returned if a response variable JsonPath or XMLPath expression does not match lease with a matching tag name is not found. Tick this option to ignore these errors, only logging a warning to the build log. This is only available if Wait for result is ticked..
Fail build on error
Tick this to fail the build if the operation returns an error or failure. This is only available if Wait for result is ticked.
Log build messages
When this is ticked, Continua CI will add messages to the build log during execution of the HTTP Request build event handler. Build log messages will only be recorded if Wait for Result is ticked.